SmartUQ is a powerful Machine Learning (ML) software tool optimally designed for science and engineering applications. By providing powerful tools and highly accurate ML models with user-friendly GUIs and APIs, SmartUQ makes it easy to perform predictive modeling, optimized sampling, uncertainty quantification, and model calibration. From Fortune 500 manufacturers to startups and engineering consulting firms, SmartUQ's best in class predictive modeling accuracy helps our customers go beyond analysis to bring uncertainty into the decision-making process.
SmartUQ's combination of unique sampling capabilities, powerful machine learning tools, and easy to use analytics help our customers solve previously unsolvable problems.
SmartUQ has significantly expanded the scope of usage in recent years to include a full range of machine learning and KI applications. Therefore, the tools can assist throughout the product lifecycle from early design idea through design analysis and review to optimization of design processes.
We would like to draw particular attention to the following features:
Design of Experiments
Emulation
Sensitiv Analysis
Statistical Calibration
Statistical Optimmization
Data Sampling
Uncertainty Propagation
Design of Experiments Overview
SmartUQ offers a suite of specialized space-filling designs, an assortment of state of the art Design of Experiments (DOEs), and several unique patent-pending DOEs for complex challenges. We understand you have two main concerns when it comes to experimental design: getting enough data to accurately represent the system being sampled and controlling costs by reducing the number of samples.
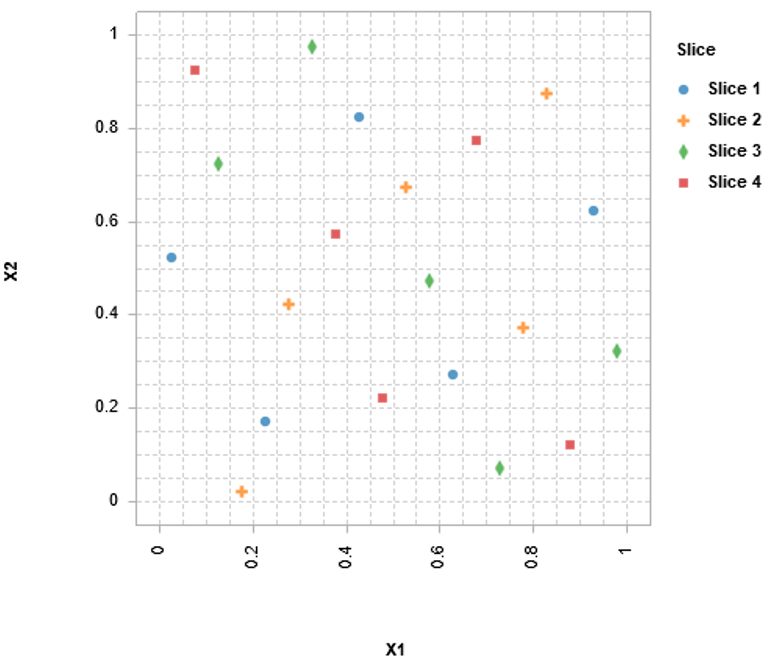

Our state of the art DOEs ensure sufficient sampling while reducing the number of points required. Our proprietary DOEs go further, using information from previously sampled points to determine where the next samples should be taken to give you the data you need to move forward. You can even think outside the box by subsampling from large observational data sets. Plus, SmartUQ’s flexible DOE generation tools let you tailor your sampling to your specific needs.
One thing is certain, when you choose SmartUQ software to design DOEs, you will have more accurate and comprehensive results with significantly fewer runs, which saves both time and money.
Emulation Overview
Statistical emulation is widely used to predict and understand the behavior of complex systems such as those found in engineering simulation and testing. The ability of emulators to rapidly predict system responses can be used for all kinds of intensive analytics such as calibration, sensitivity analysis, and uncertainty propagation.
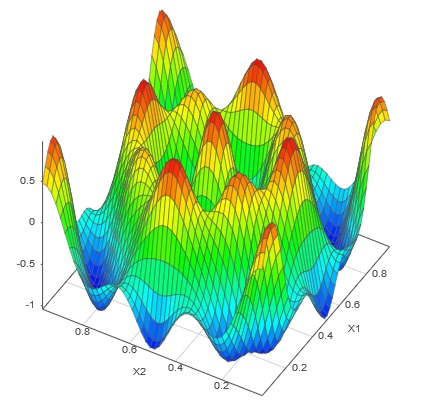
SmartUQ's breakthrough emulation algorithms dissolve barriers to fitting emulators to big data sets and high dimensional systems, opening new possibilities for the use of uncertainty quantification and analytics. Our patent-pending technologies easily handle continuous and discrete inputs, and can build lightweight emulators with univariate, multivariate, transient, and functional outputs. It does all this at lightning speed.
Sensitivity Analysis Overview
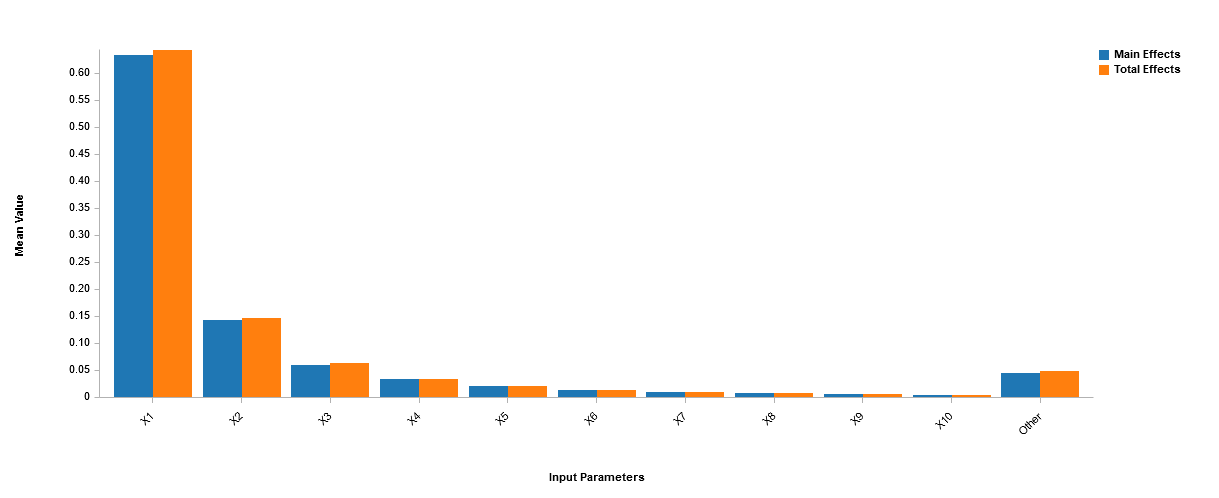
Sensitivity analysis quantifies the variation in the outputs of a simulation model with respect to changes in simulation inputs. Using information obtained from sensitivity analysis can help determine which inputs are the most relevant and which might be neglected. Knowing which inputs are important can help highlight potential problems early, refine models to be more accurate or efficient, and narrow the search space used in design and optimization. Considering fewer factors can drastically reduce the necessary number of samples, reducing costs and saving time. These abilities make sensitivity analysis crucial when handling complex systems and creating robust solutions.
SmartUQ features two proven sensitivity analysis solutions: emulation based and generalized Polynomial Chaos Expansion (gPCE).
Statistical Calibration Overview
The use of simulations to displace physical tests has become essential in accelerating analysis and reducing the cost of research and design. However, simulation results may be different from reality and it is critical to use statistical calibration and model validation to make the best use of limited test data in grounding models. The potential to reduce design cycle time and costs savings by ensuring that simulations are as close to reality as possible have never been greater.
Statistical Optimization Overview
Using a combination of proprietary adaptive DOEs and our breakthrough emulators, statistical optimization rapidly evaluates the design space and makes predictions about promising regions.
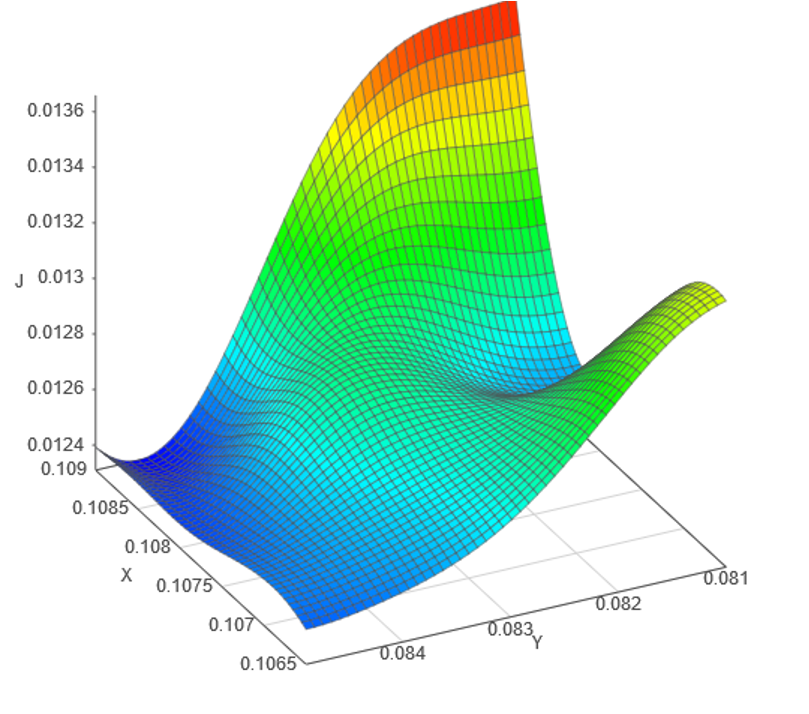
Statistical optimization works well with both low and high-dimensional problems. Our software minimizes the number of simulation runs required to get optimal results for a wide variety of problems and is capable of handling a large number of input and output types including binary and discrete, multiple constraints, and optimization with multiple goals.
With statistical optimization in SmartUQ, you can use an iterative DOE based sampling technique to improve knowledge of both the entire design space and regions likely to contain optimal points. Running sampling DOEs in parallel batches, instead of running single points in sequence, allows full use of computing resources and can deliver answers hundreds of times faster.
As an added benefit, significant savings can be achieved by using the same system evaluations for finding optimums as well as for analytics and UQ analysis of the optimization results. Not only can you explore optimal regions of the design space, you can determine how sensitive optimums are to changes in input parameters and whether variations around optimal points might lead to unexpected or undesirable behavior such as constraint violations.
Combinations of statistical optimization and search based optimization functions, such as genetic algorithms, can be used to take advantage of the best properties of both.
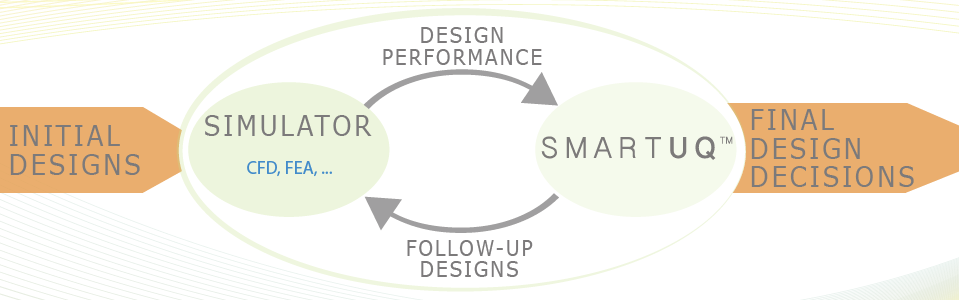 Figure 1: Statistical Optimization Flow Chart
Figure 1: Statistical Optimization Flow Chart
Data Sampling
DOEs are typically used to collect new data from a system. In many cases, sufficient data has already been collected. Often in these scenarios, the data collected has been accumulated over long periods of time, and there is enough data that analysis is simply intractable. For example, health monitoring data from sensors on fielded components may capture live data continuously over the entire operating life of the component. SmartUQ’s data sampling tools can divide the data to mimic a space-filling DOE consisting of subsets of the full data set. Unlike DOEs which are developed before data collection, data sampling like subsampling and sliced sampling takes existing input-output data pairs and selects the points that will represent the design space well.
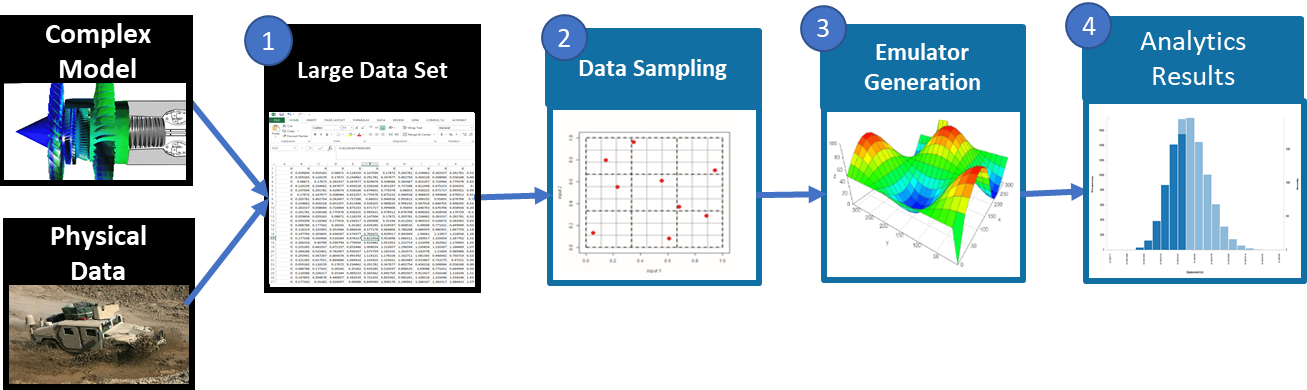 Data Sampling Workflow
Data Sampling Workflow
The workflow of data sampling tool starts with a collected data set from simulation and/or physical data. The data set tends to be large, and using the whole data set to perform analysis may be computationally demanding. SmartUQ data sampling tools can divide the data set in a smaller subset that represents the design space well.
Propagation of Uncertainty Overview
Propagation of uncertainty calculates the effects of the uncertainty in system inputs on the system outputs. This information is critical when quantifying confidence in a system's outputs.
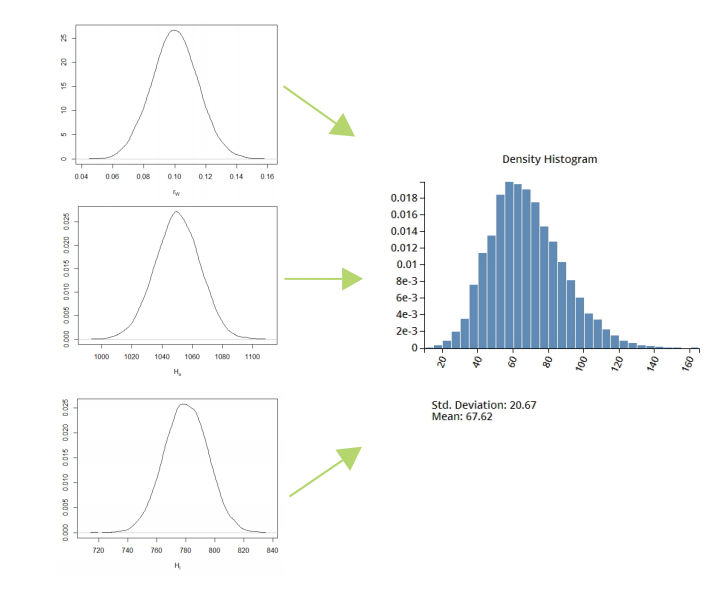
Propagation of uncertainty helps determine whether system outputs will meet requirements given the anticipated variation in inputs. This makes it possible to estimate the probabilities of outcomes, to cost effectively determine required tolerances, and to predict more failures before they happen.
SmartUQ delivers advanced stochastic mathematics in an easy-to-use tool and features two ways of calculating propagation of uncertainty, emulator based and generalized Polynomial Chaos expansion (gPCE).



