Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consetetur sadipscing elitr, sed diam nonumy eirmod tempor invidunt ut labore et dolore magna aliquyam erat, sed diam voluptua
NCSS
Produktinformationen "NCSS"
📊 NCSS – Ihre leistungsstarke Statistiksoftware für umfassende Datenanalysen
🚀 NCSS: Das All-in-One-Statistikpaket für Ihre Datenanalyse
NCSS ist eine vielseitige Statistiksoftware, die Ihnen leistungsstarke Werkzeuge für Datenanalyse, Prognosen und statistische Modellierung bietet. Egal ob deskriptive Statistik, Regressionsanalyse, Versuchsplanung (DoE) oder statistische Prozesskontrolle (SPC) – mit NCSS haben Sie alle Funktionen, die Sie für fundierte Analysen benötigen.
🌟 Warum NCSS?
✅ Umfassendes Statistikpaket – von deskriptiven Methoden bis zu komplexen Modellierungen.
✅ Intuitive Menüführung – Finden Sie schnell die passende Methode für Ihr Problem.
✅ Hochwertige Datenvisualisierung – Aussagekräftige Grafiken für präzise Analysen.
✅ Detaillierte Hilfe & Lernressourcen – Umfangreiche Dokumentation & Trainingsvideos.
🔍 Leistungsstarke Funktionen für Ihre Analysen
📈 Datenanalyse & Statistik:
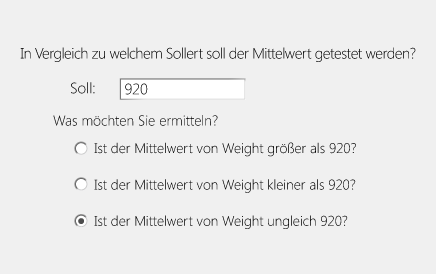
✔ Deskriptive Statistik & Mittelwertvergleiche für eine fundierte Datenbewertung.
✔ Regressionsanalysen – Von linear bis verallgemeinert (GLM) für präzise Vorhersagen.
✔ Zeitreihenanalyse & ARIMA-Modelle – Zukunftsprognosen auf Basis historischer Daten.
🔬 Fortgeschrittene Methoden:
✔ Versuchsplanung (DoE) – Optimierung von Produkten & Prozessen.
✔ Clusteranalysen – Identifizieren Sie Muster & Strukturen in großen Datensätzen.
✔ Überlebenszeitanalysen (Kaplan-Meier) – Zuverlässigkeit & Risikobewertungen.
📊 Datenvisualisierung & Berichterstellung:
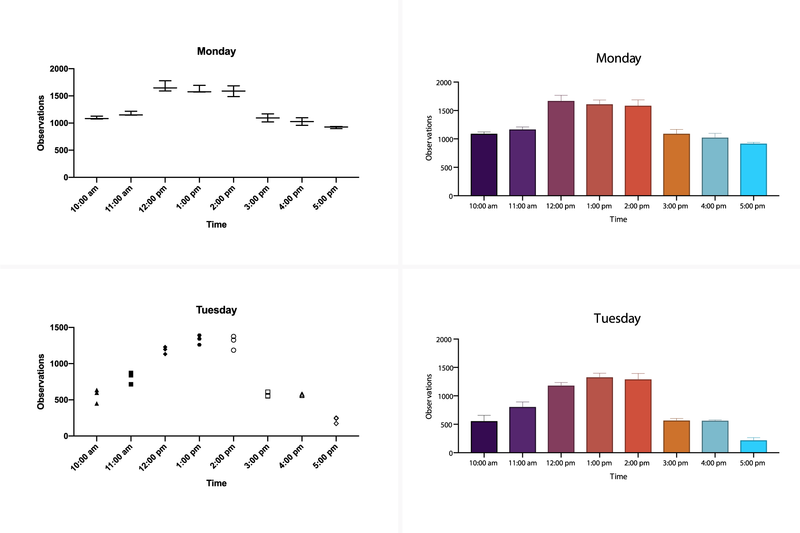
✔ Dynamische Diagramme & Grafiken zur besseren Interpretation Ihrer Ergebnisse.
✔ Automatisierte Berichte für eine professionelle Präsentation der Analysen.
🎯 NCSS – Die richtige Wahl für Experten & Einsteiger
Ob für Wissenschaftler, Datenanalysten oder Qualitätssicherungs-Profis – NCSS bietet leistungsfähige Werkzeuge für jede statistische Herausforderung.
📢 Jetzt NCSS entdecken und Ihre Datenanalyse auf das nächste Level bringen!
NCSS – Die leistungsstarke Statistik-Software für präzise Datenanalysen
NCSS: Umfassende und benutzerfreundliche Statistik-Software
NCSS ist ein leistungsstarkes und intuitives Statistik-Softwarepaket, das umfassende Analyse- und Visualisierungsfunktionen bietet. Mit über 150 statistischen und grafischen Tools ermöglicht NCSS eine präzise Datenauswertung für Wissenschaft, Forschung und Unternehmen.
Vorteile von NCSS auf einen Blick:
✔ Umfassend & genau – Hochwertige Analysewerkzeuge für präzise Ergebnisse
✔ Preisgünstig – Erstklassige Statistik-Software zum fairen Preis
✔ Benutzerfreundlich – Intuitive Bedienung, ideal für Einsteiger & Experten
✔ Kompatibilität – Unterstützt Windows XP/Vista, 7, 8, 10 (32 & 64 Bit)
✔ Flexible Datenverarbeitung – Import/Export gängiger Dateiformate (Excel, CSV, SQL & mehr)
✔ Leistungsstark – Verarbeitung großer Datenmengen (über 1.000 Variablen, 200.000 Zeilen)
✔ Integration & Export – Direkter Export in Word, PowerPoint & andere Programme
NCSS – Statistische Analysen leicht gemacht
Mit NCSS lassen sich aussagekräftige numerische Ergebnisse und hochwertige Grafiken in wenigen Schritten erstellen:
-
Daten importieren oder manuell eingeben – Unterstützung aller wichtigen Statistik-Formate
-
Analyseverfahren auswählen – Drop-Down-Menü, Suchfunktion oder Kategoriebaum nutzen
-
Datenbereiche definieren & Analyse starten – Klare & leicht interpretierbare Ergebnisse erhalten
Erweiterte Funktionen für anspruchsvolle Analysen
✅ Intuitives Datenmanagement – Effiziente Filter- und Transformationsfunktionen
✅ Benutzerfreundliche Oberfläche – Eingebaute Hilfen für jeden Analyseschritt
✅ 80+ anpassbare Plots – Detaillierte Visualisierungen mit anpassbarem Layout
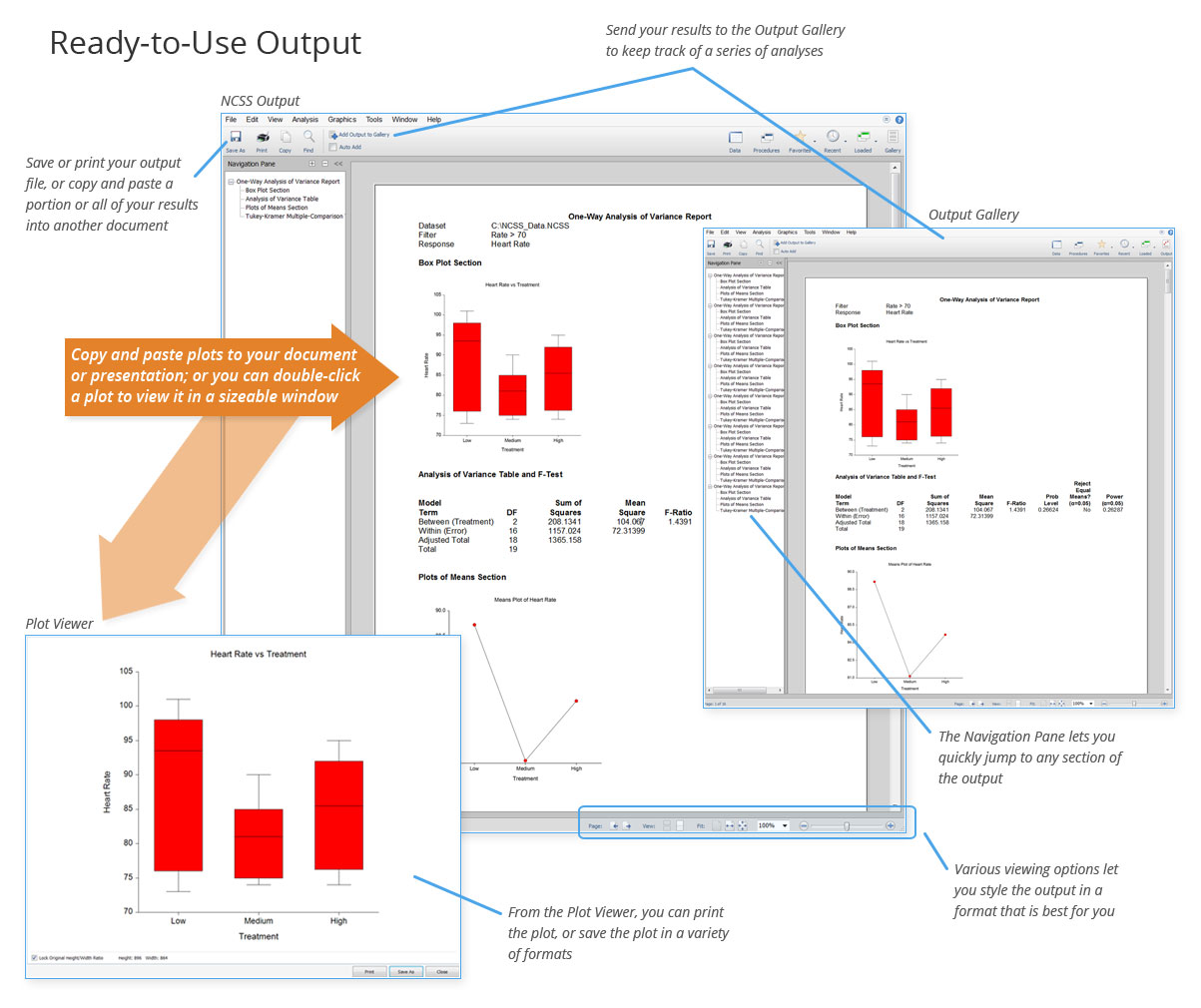
✅ Ready-to-Use Output – Ergebnisse sofort speichern, exportieren & weiterverarbeiten
Nutzen Sie die vielseitigen Funktionen von NCSS, um fundierte Entscheidungen auf Basis präziser Datenanalysen zu treffen!
📌 Mehr erfahren auf der offiziellen NCSS-Website: [NCSS Homepage]
Minimum System Requirements for NCSS
These are the computer requirements in order to run NCSS 12 Statistical Analysis Software:
- Processor:
- 450 MHz or faster processor
- 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) processor
- RAM:
- 256 MB (512 MB recommended)
- Operating Systems:
- Windows XP with Service Pack 2 or higher
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows 8 and 8.1
- Windows 10 or later
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2 or later
- Privileges:
- Administrative rights required during installation only
- Third Party Software:
- Microsoft .NET 3.5 SP1 (included with NCSS CD, comes pre-installed with Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, feature activation required on Windows 8, 8.1, 10 and Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2)
- Microsoft Windows Installer 3.1 or higher
- Adobe Reader® 7 or higher (required for the Help System only)
- Hard Disk Space:
- 160 MB for NCSS (plus space for Microsoft .NET 3.5 SP1 if not already installed)
- Printer:
- Any Windows-compatible inkjet or laser printer
NCSS unter MAC OS X
Für den Betrieb von NCSS unter Mac OS X ist ein Windows Emulator, wie z.B. Parallels notwendig!
Details
Minimum System Requirements for NCSS
These are the computer requirements in order to run NCSS 12 Statistical Analysis Software:
- Processor:
- 450 MHz or faster processor
- 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) processor
- RAM:
- 256 MB (512 MB recommended)
- Operating Systems:
- Windows XP with Service Pack 2 or higher
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows 8 and 8.1
- Windows 10 or later
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2 or later
- Privileges:
- Administrative rights required during installation only
- Third Party Software:
- Microsoft .NET 3.5 SP1 (included with NCSS CD, comes pre-installed with Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, feature activation required on Windows 8, 8.1, 10 and Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2)
- Microsoft Windows Installer 3.1 or higher
- Adobe Reader® 7 or higher (required for the Help System only)
- Hard Disk Space:
- 160 MB for NCSS (plus space for Microsoft .NET 3.5 SP1 if not already installed)
- Printer:
- Any Windows-compatible inkjet or laser printer
NCSS unter MAC OS X
Für den Betrieb von NCSS unter Mac OS X ist ein Windows Emulator, wie z.B. Parallels notwendig!